Lois normales - Calculatrice
Calculatrice
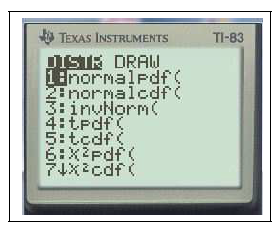
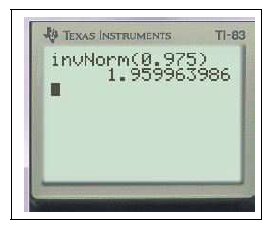
- Calcul de $u_{\alpha}$ :
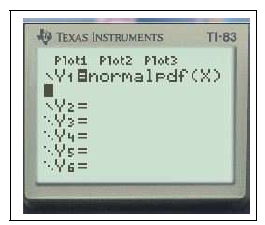
- Fonction densité :
- $\Pi(t)$:
- Pour la loi binomiale :
2ndDISTR3FracNormale(0,975)EXE
$FracNormale(0,975)\approx 1,96$
|
|
|
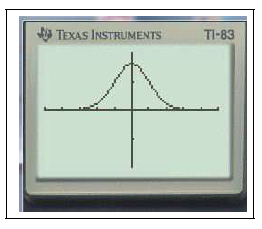
$Y_1=$normalFdp(X)graphezoom0:ZMinMax
|
|
|
|
|
|
Par exemple pour afficher la densité de la loi normale $\mathcal{N}(2,1)$; on tape :
$Y_1=$normalFdp(X,2,1)graphezoom
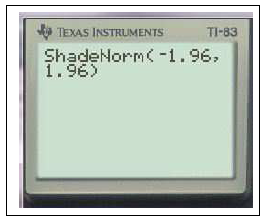
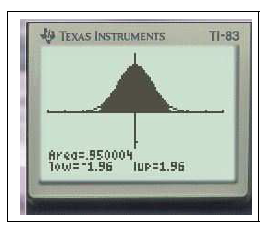
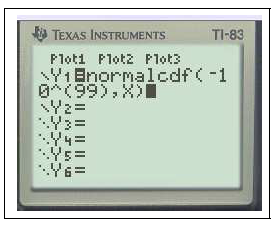
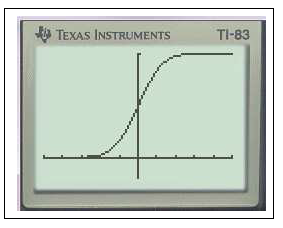
$Y_1=$normalFRép(-10,X)graphezoom
En effet on peut remarquer que $f(-10)\approx 7,7.10^{-23}$ ou encore avec un logiciel de calcul formel ( Maple) on obtient $\displaystyle\lim_{a\to -\infty}\int_a^{-10} f(x) \;dx\approx 7.10^{-24}$
|
|
|
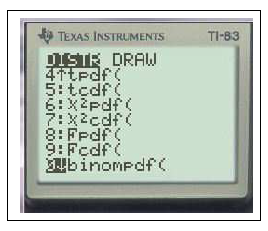
2ndDISTR0binomFdp(
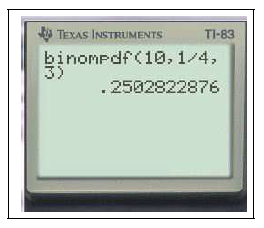
$binomFdp(10,0.25,3)\approx 0.25$
Ceci calcule $P(X=3)$ dans le cas où $X$ suit la loi binomiale $\mathcal{B}(10,0.25)$
|
|
|
$binomFdp(10,0.25,3)\approx 0.25$
Ceci calcule $P(X=k)$ pour $k =3$ dans le cas où $X$ suit la loi binomiale $\mathcal{B}(10,0.25)$
2ndDISTR0binomFdp(
$binomFdp(10,0.25)$ Ceci calcule la liste des probabilités $P(X=k)$ pour $k \in\{0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10\}$ dans le cas où $X$ suit la loi binomiale $\mathcal{B}(10,0.25)$
Cela fournit donc la loi de probabilité de cette variable aléatoire.
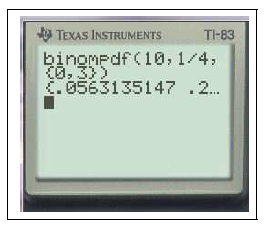
$binomFR\text{é}p(10,0.25,3)\approx 0.78$
Ceci calcule la probabilité $P(X\leq 3)$ dans le cas où $X$ suit la loi binomiale $\mathcal{B}(10,0.25)$
2ndDISTR0binomFRép(
$binomFR\text{é}p(10,0.25)$
Ceci calcule la liste des $P(X\leq k)$( $0\leq k\leq 10$) dans le cas où $X$ suit la loi binomiale $\mathcal{B}(10,0.25)$
Exercice
Soit $X$ une variable aléatoire suivant $\mathcal{B}(10,0.25)$
Calculer de deux façons différentes $P(2\leq X\leq 7)$
Exercice
On lance indépendamment $400$ fois une pièce équilibrée. On note $X$ le nombre de résultats « face» et $\tilde X$ la variable aléatoire centrée réduite correspondante.
Montrer que $P(190\leq X\leq 220)= P(-1\leq \tilde X\leq 2)$. Estimer alors $ P(190\leq X\leq 220)$
- Vues: 23420